

It may be seen along with complete or partial malformation of the pinna (outer ear) and is noted at birth. Atresia of the Ear Canal: Complete malformation of the external ear canal is called atresia.In rare cases these lesions require surgical removal. These bony lesions can generally be managed with vigilant cleaning of ear wax to prevent obstruction. Bony lesions of Ear Canal: These are benign growths of bone along the walls of the ear canal resulting in a narrowing of the ear canal which may then lead to frequent obstruction from a small amount of wax or water.Uncommonly, the foreign object is a live bug such as a cockroach which can cause itching, pain and noise.
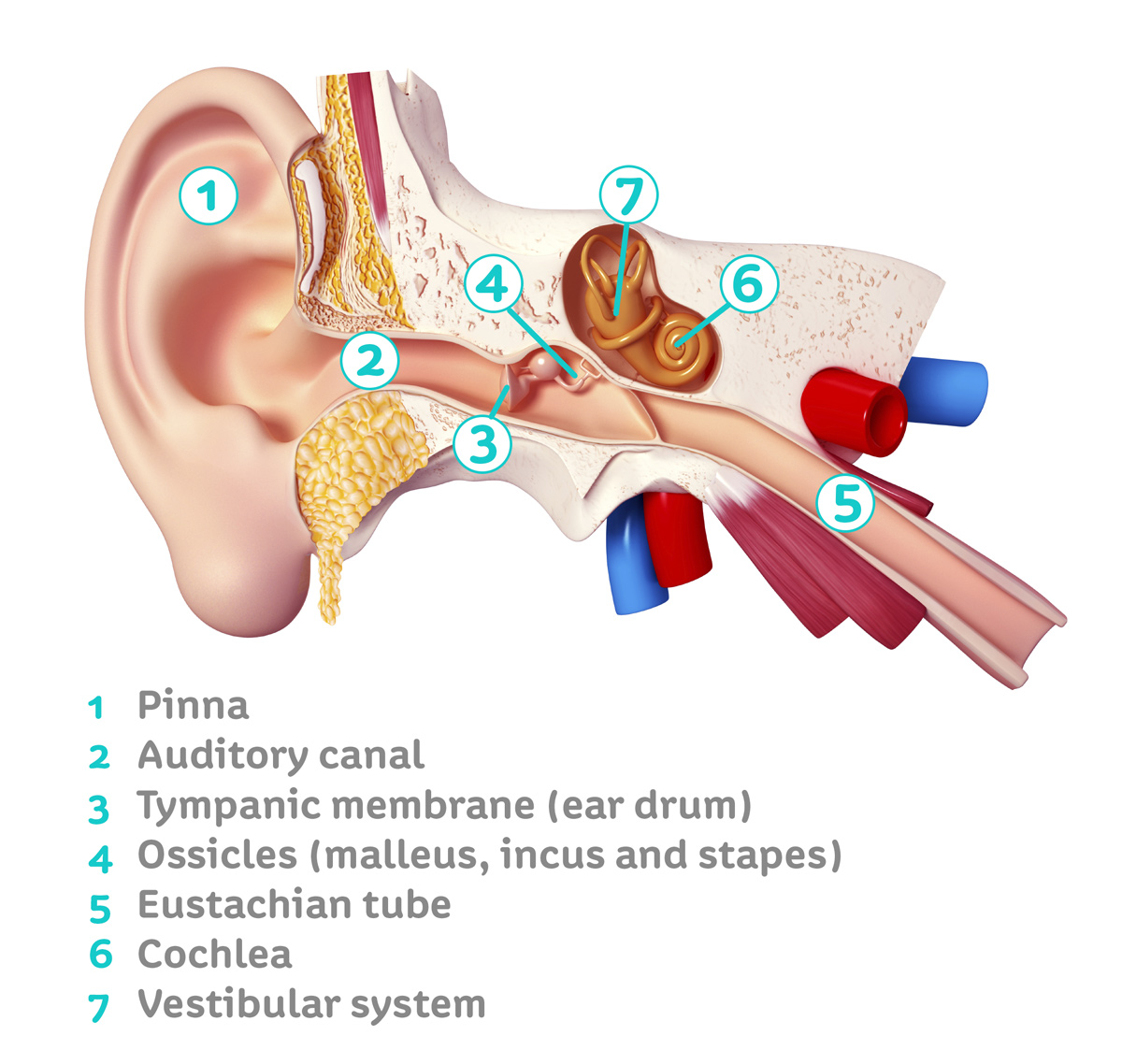
Common foreign bodies include beads and beans in children and cotton or the tips of cotton-tipped applicators in adults. Occasionally, a brief anesthesia is required for this procedure in children. Foreign body in Ear Canal: This is also readily identified on examination and can usually be cleared in the office.Although the most common symptoms of otitis externa are pain and tenderness of the ear, conductive hearing loss can also occur if there is severe swelling of the ear canal. Otitis Externa: Often referred to as “swimmer’s ear”, an infection of the ear canal may be related to water exposure.This condition may actually be aggravated by cotton tipped applicators (Q-tips) that many patients use in an attempt to clean their ears. Cerumen (ear wax) obstruction: Ear wax can be identified by a medical examination and can usually be removed quickly.Some of the causes of conductive hearing loss include: PROBLEMS WITH THE EXTERNAL EAR WHAT CAN CAUSE CONDUCTIVE HEARING LOSS?Ĭonductive hearing loss may result from diseases that affect the external ear or middle ear structures. An otolaryngologist, also called an Ear Nose and Throat or ENT doctor, can determine the specific diagnosis and treatments for either type of hearing loss and perform surgical treatments, if necessary. The distinction between these two types of hearing loss is important because many cases of conductive hearing loss can be improved with medical or surgical intervention. A formal audiogram, or hearing test, is the best way to determine the type and degree of hearing loss. The preliminary classification of hearing loss as conductive or sensorineural can be determined by a physician using a tuning fork in the office. Mixed hearing loss refers to a combination of these two types. Hearing loss can be divided into two types: Conductive Hearing Loss, which is essentially a mechanical problem with the conduction of sound vibrations, and Sensorineural Hearing Loss, a problem with the generation and/or transmission of nerve impulses from the inner ear to the brain. The sound vibrations in the ossicles are then transmitted to the nerves and fluids in the cochlea (inner ear), which generates a nerve impulse that passes along the auditory nerve to the brain. Sound waves enter the ear canal and cause a vibration of the tympanic membrane (ear drum) which is then passed through three tiny bones behind the ear drum in the middle ear space: the malleus (hammer), incus (anvil) and stapes (stirrup). The ear can be divided into three parts: 1) the external ear includes the pinna (outer, visible ear) and the ear canal, 2) the middle ear includes the tympanic membrane (ear drum) and the ossicles (middle ear bones), 3) the inner ear, which includes the cochlea (organ of hearing) and vestibule (organ of balance).
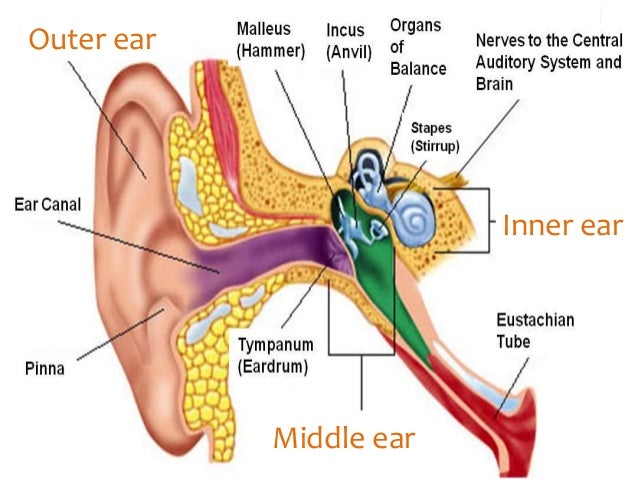
Conductive Hearing Loss: Causes and Treatments HOW DOES THE EAR HEAR SOUNDS?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
